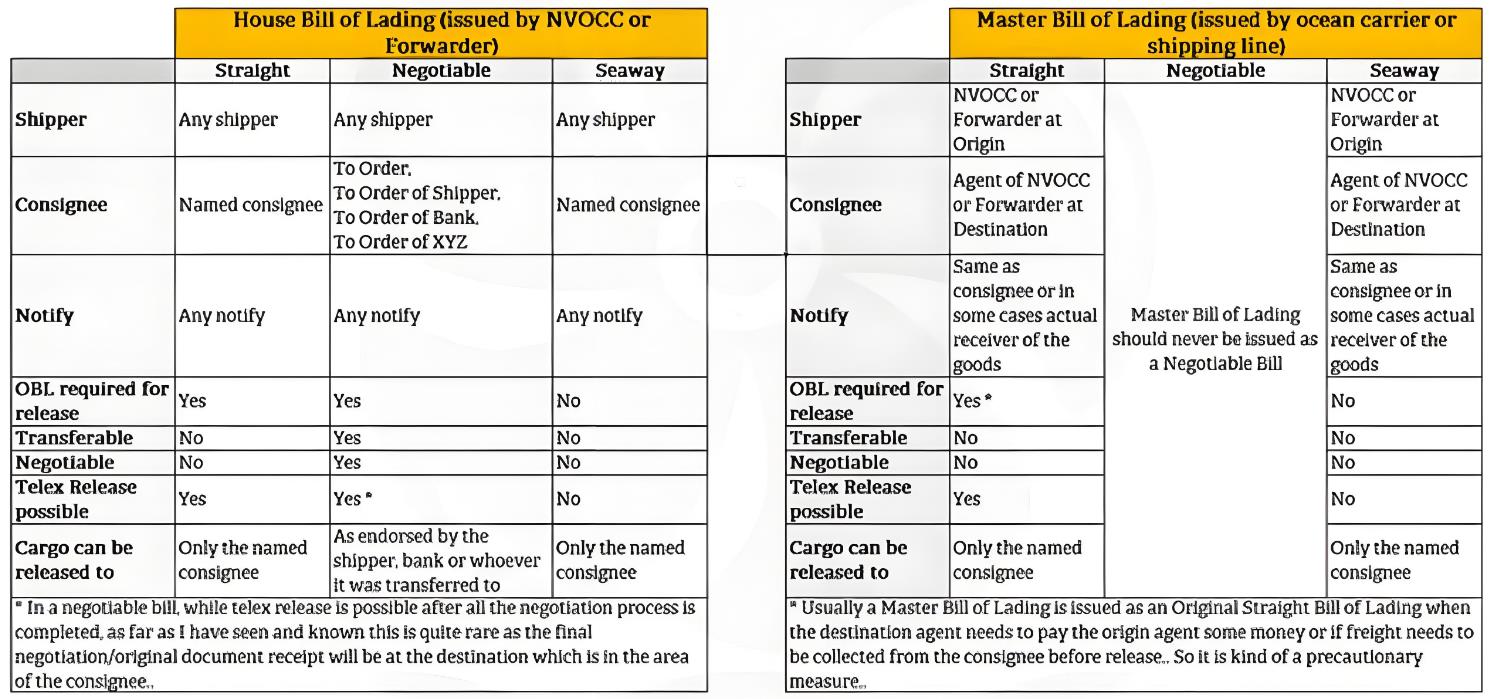
What Is The Difference Between HBL And MBL In International Trade
In the realm of international cargo transportation, the bill of lading (B/L) is a document of paramount importance, serving as both a legal instrument signifying ownership of the goods and a formal proof of the transportation contract. Typically, bills of lading are categorized into two distinct types: the master bill of lading (MBL) and the house bill of lading (HBL). This article aims to provide
This article may help you: The 11 Common International Trade Logistics Terms
Introduction to MBL
The Master Bill of Lading (MBL) stands as a fundamental document within the sphere of maritime cargo transportation. Issued by the shipping company or its duly authorized agent, it meticulously delineates comprehensive information pertaining to the goods, including details regarding the consignor, consignee, the quantity of goods, the method of packaging, and the ports of loading and unloading. The MBL serves a dual purpose: it not only acts as a certificate attesting to the ownership of the goods but also functions as a crucial document that establishes the rights, property, and liability relationships among all consignors, thereby embodying the characteristics of a property rights certificate.
Introduction to HBL
HBL, or House Bill of Lading, is a certificate issued by a freight forwarder to the consignor when undertaking cargo transportation business. HBL records in detail the key information such as the name, quantity, place of departure and destination of the goods, and is an indispensable and important document in international trade. It proves that the freight forwarder has accepted the consignor’s entrustment and promised to deliver the goods to the designated destination in accordance with the requirements of the transportation contract.
Applicable situations of MBL and HBL
MBL is applicable to full container shipping (FCL). It is the highest document in the international transportation of goods, carrying important information about the goods and is irreplaceable. For sea transportation, MBL is proof of the transportation contract between the cargo owner and the shipping company, ensuring the cargo owner’s control and rights over the goods.
HBL can be used for both full container shipping and less than container shipping (LCL). In LCL transportation, since the shipping company will not issue a LCL bill of lading, only HBL can be used. In addition, when there are middlemen, the middlemen may keep business secrets by issuing HBL to prevent the end customer from knowing key information such as the source of the goods.
Differences between HBL and MBL
Although HBL and MBL have some similarities, their functions and legal implications are very different:
| Differences | Master Bill of Lading (MBL) | House Bill of Lading (HBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Carrier or shipping company | Freight forwarder/NVOCC |
| Purpose | Represents entire shipment | Represents individual shipments |
| Legal Status | Acts as a contract | Acts as a receipt |
| Negotiability | Typically non-negotiable | Can be negotiable |
| Usage | For customs and tracking | For detailed cargo info |
| Ownership | Between exporter and consignee | Between carrier and freight forwarder |
Frequently Asked Questions about MBL and HBL
In international transportation, can HBL and MBL be reused?
Generally speaking, MBL, as a contract between the carrier and the shipper, is unique and cannot be copied. HBL, as an operating document between the parties in the transportation process, can have multiple HBLs corresponding to one MBL, especially in the case of multimodal transport.
Bill of Exchange Fees
When HBL is exchanged for MBL at the destination port, bill of exchange fees may be involved, and the amount is not fixed.
When is HBL needed?
HBL is usually used in the case of multimodal transport, especially when the goods are transported by multiple carriers (such as shipping, air transport, land transport, etc.), and the freight forwarding company will provide HBL for different shippers.
Is it easy to modify HBL and MBL?
The modification of MBL usually requires negotiation with the carrier, and the modification procedure is relatively complicated. The modification of HBL is usually carried out by the freight forwarding company and is relatively easy to handle.
Learn more:How is the Terminal Handling Charge (THC) calculated?
In international trade, master bill of lading (MBL) and intermediate bill of lading (HBL) respectively symbolize the contractual agreements between the carrier and the shipper, as well as between the shipper and the freight forwarder. As a professional freight forwarder in China, Presou Logistics has an obligation to ensure that global freight forwarders understand the differences between these two documents, which is crucial for effective management and control of the transportation process of goods.
 English
English 简体中文
简体中文 繁體中文
繁體中文 Afrikaans
Afrikaans አማርኛ
አማርኛ Español
Español العربية
العربية Français
Français Dansk
Dansk Български
Български Беларуская мова
Беларуская мова বাংলা
বাংলা Português
Português Русский
Русский Afsoomaali
Afsoomaali فارسی
فارسی Türkçe
Türkçe كوردی
كوردی Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 ไทย
ไทย Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano עִבְרִית
עִבְרִית 한국어
한국어 Română
Română Nederlands
Nederlands Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Shona
Shona